Why Do Horses Bob Their Heads: Understanding This Common Equine Behavior
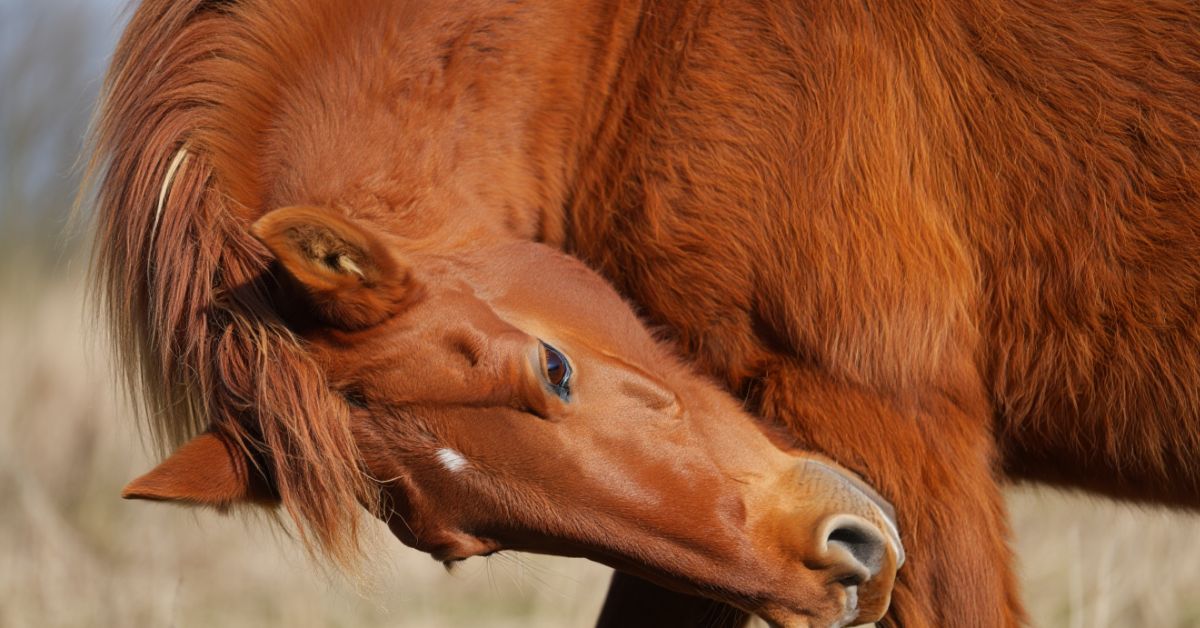
Horse head bobbing is one of the most intriguing and sometimes concerning behaviors that horse owners encounter. Whether you're a seasoned equestrian or new to the horse world, understanding why do horses bob their heads is crucial for proper horse care and welfare. This rhythmic movement can range from perfectly normal behavior to a sign of underlying health issues that require immediate attention.
Head nodding in horses occurs for various reasons - from simple fly irritation to complex neurological conditions. Some horses develop stereotypic behaviors in horses as a coping mechanism, while others may exhibit horse head movement due to physical discomfort or pain-related head bobbing. As passionate horse enthusiasts at Dream Horse, we understand how concerning it can be to see your beloved equine companion displaying unusual behaviors.
This comprehensive guide will explore every aspect of equine head bobbing, helping you distinguish between harmless habits and serious health concerns. We'll cover everything from behavioral head bobbing to horse lameness head bobbing, ensuring you have the knowledge to make informed decisions about your horse's well-being. 🐴
Chapter 1: Understanding Normal vs. Abnormal Horse Head Bobbing
What is Normal Horse Head Bobbing?
Horse head bobbing in its natural form is simply part of equine communication and daily behavior. Horses use head movements and pain signals differently than humans might expect. When horses graze, walk, or interact with their environment, slight horse head movement is completely normal and healthy.
Natural head nodding in horses typically occurs during:
-
Grazing and foraging activities
-
Social interactions with other horses
-
Fly and insect deterrence
-
General alertness and environmental scanning
However, abnormal horse behavior becomes apparent when the head bobbing is repetitive, excessive, or occurs without obvious triggers. Horse behavior head bobbing that persists for extended periods or interferes with normal activities requires closer examination.
Recognizing Concerning Patterns
Stereotypic behaviors in horses often develop as stress responses or coping mechanisms. Unlike natural movements, these behaviors are repetitive, serve no obvious function, and may indicate underlying welfare issues. Equine head bobbing becomes problematic when it's rhythmic, compulsive, and occurs regardless of the horse's environment or activities.
According to equine behavior specialists, approximately 15% of domesticated horses develop some form of stereotypic behavior, with head bobbing while standing being among the most common manifestations. This statistic highlights the importance of proper horse welfare and environmental enrichment for horses.
The Role of Individual Personality
Just like humans, horses have unique personalities that influence their behavior patterns. Some horses are naturally more active and expressive, while others remain calm and reserved. Understanding your horse's baseline behavior is essential for recognizing when horse head bobbing becomes abnormal.
Dream Horse's equestrian jewelry collection celebrates these individual horse personalities - much like how each horse expresses themselves differently, our pieces allow riders to express your style and connect with your equine passion. 💎
Chapter 2: Common Causes of Horse Head Bobbing
Physical Discomfort and Pain
Pain-related head bobbing is often the first concern veterinarians investigate when examining horses with persistent head movements. Horse lameness head bobbing typically presents as a rhythmic up-and-down motion that corresponds with the horse's gait or weight-bearing.
Dental Issues
Dental problems frequently cause head bobbing while eating or shortly after meals. Sharp points, infected teeth, or improper wear patterns can create significant discomfort, leading horses to develop compensatory head movements.
Neurological Conditions
Horse neurological issues can manifest as various forms of equine head bobbing. Headshaking syndrome, a complex neurological condition, affects approximately 1-5% of horses and can cause violent, uncontrollable head movements that significantly impact the horse's quality of life.
Musculoskeletal Problems
Neck pain, muscle tension, and spinal alignment issues often contribute to physiological head bobbing. These conditions may develop gradually, making them challenging to identify until the behavior becomes pronounced.
Environmental and Management Factors
Stress in horses and anxiety in horses frequently manifest through various stereotypic behaviors, including persistent horse head movement. Poor management practices, inadequate turnout, or social isolation can trigger these responses.
Stable Environment Issues
-
Limited movement and exercise opportunities
-
Insufficient social interaction with other horses
-
Inadequate environmental enrichment for horses
-
Inconsistent feeding schedules
-
Excessive confinement periods
Boredom and Understimulation
Boredom in horses is a significant contributor to stable vices and horse stereotypic behavior. Horses are naturally active animals that require mental and physical stimulation to maintain psychological well-being.
Learned and Compulsive Behaviors
Equine compulsive behaviors often develop as coping mechanisms but can persist even after the original trigger is removed. Head bobbing while standing may become so ingrained that horses continue the behavior automatically, similar to how humans develop nervous habits.
Research from the University of California, Davis (2019) found that horses displaying stereotypic behaviors often have altered brain chemistry, particularly in areas related to reward and pleasure responses. This finding emphasizes the complexity of managing horse behavior and the importance of addressing root causes rather than just symptoms.
Chapter 3: Identifying Different Types of Head Bobbing Patterns
Rhythmic and Repetitive Movements
Stereotypic behaviors in horses typically display consistent patterns that distinguish them from natural movements. Horse head bobbing associated with weaving and head bobbing often occurs in predictable cycles, with horses maintaining steady rhythms for extended periods.
The most common stereotypic patterns include:
-
Vertical head bobbing: Up-and-down movements while standing or moving
-
Lateral head shaking: Side-to-side movements, often associated with headshaking syndrome
-
Combination movements: Complex patterns involving both vertical and horizontal components
-
Speed variations: Some horses alternate between slow, deliberate movements and rapid, frantic bobbing
Context-Dependent Head Bobbing
Head bobbing while walking versus head bobbing in the pasture can provide valuable diagnostic clues about underlying causes. Movement-related head bobbing often indicates lameness or discomfort, while stationary bobbing suggests behavioral or neurological origins.
Exercise-Related Patterns
Horse lameness head bobbing typically worsens with increased activity and may be more pronounced on specific surfaces or during particular gaits. Observing these patterns helps veterinarians pinpoint the source of discomfort and develop appropriate treatment plans.
Environmental Triggers
Some horses only exhibit equine head bobbing in specific situations, such as during feeding time, when other horses are present, or in response to certain sounds or activities. Identifying these triggers is crucial for horse behavior head bobbing management.
Associated Behaviors and Comorbidities
Horse head bobbing rarely occurs in isolation. Many horses displaying this behavior also exhibit other stable vices such as cribbing and head bobbing or pacing and head bobbing. Understanding these relationships helps create comprehensive treatment approaches.
As Dr. Katherine Houpt, renowned equine behaviorist, states: "Stereotypic behaviors in horses are like pieces of a puzzle - understanding one behavior often provides insights into the horse's overall welfare and management needs."
The interconnected nature of these behaviors reflects the complexity of understanding horse communication and the importance of holistic approaches to equine veterinary advice. Just as Dream Horse's practical accessories work together to enhance the riding experience, addressing multiple aspects of horse welfare simultaneously produces the best outcomes.
Chapter 4: Health Implications and Associated Conditions
Serious Medical Concerns
Horse neurological issues represent some of the most serious causes of equine head bobbing. Headshaking syndrome can severely impact a horse's quality of life and may require specialized veterinary intervention. This condition affects horses of all ages and breeds, though certain lines show higher susceptibility.
Progressive Conditions
Some neurological causes of horse head movement are progressive, meaning they worsen over time without proper treatment. Early identification and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent further deterioration.
Secondary Health Effects
Chronic horse head bobbing can lead to additional health problems, including neck muscle fatigue, dental wear patterns, and difficulty eating or drinking normally. These secondary effects emphasize the importance of addressing abnormal horse behavior promptly.
Impact on Performance and Quality of Life
Horse behavior head bobbing significantly affects a horse's ability to perform normal activities. Riding becomes challenging or impossible when head movements are severe, and even basic functions like grazing may be impaired.
Training and Riding Implications
Horse training issues often develop when horses exhibit persistent stereotypic behaviors. Riders may struggle to maintain proper communication and control, leading to safety concerns and reduced performance quality.
Social and Herd Dynamics
Horses displaying equine compulsive behaviors may experience social isolation within their herd. Other horses sometimes avoid or show aggression toward individuals with pronounced stereotypic behaviors, further impacting welfare.
Long-term Prognosis and Management
Research from the Animal Welfare Institute (2020) indicates that early intervention for horse stereotypic behavior significantly improves long-term outcomes. Horses receiving prompt attention and appropriate treatment show better responses than those with established, long-standing behaviors.
Successful managing horse behavior requires understanding that head bobbing diagnosis is often just the beginning of a comprehensive welfare improvement process. Like choosing the perfect piece from Dream Horse's equestrian decoration collection to complement your space, addressing head bobbing requires careful consideration of multiple factors working in harmony.
The prognosis varies significantly depending on the underlying cause:
-
Behavioral causes: Generally good with proper management changes
-
Dental/medical issues: Excellent when underlying problems are resolved
-
Neurological conditions: Variable, depending on specific diagnosis and severity
-
Chronic stereotypic behaviors: Challenging but manageable with dedicated intervention
Chapter 5: Prevention, Treatment, and Management Strategies
Veterinary Diagnosis and Assessment
Proper head bobbing diagnosis begins with comprehensive veterinary examination. Equine veterinary advice typically involves systematic evaluation of potential causes, starting with the most common and treatable conditions.
Diagnostic Procedures
Modern veterinary medicine offers various tools for investigating horse health head bobbing:
-
Complete physical and neurological examinations
-
Radiographic imaging of head, neck, and spine structures
-
Blood work to identify underlying medical conditions
-
Behavioral assessment and environmental evaluation
-
Specialized testing for headshaking syndrome and other neurological conditions
Treatment Approaches
Treatment for head bobbing varies dramatically depending on the underlying cause. Success rates improve significantly when treatments address root causes rather than simply managing symptoms.
Medical Interventions
-
Anti-inflammatory medications for pain-related conditions
-
Neurological medications for horse neurological issues
-
Dental procedures to correct oral health problems
-
Specialized treatments for headshaking syndrome
Environmental Modifications
Environmental enrichment for horses plays a crucial role in preventing and managing behavioral head bobbing. Simple changes can produce dramatic improvements in horse welfare and behavior.
Effective environmental strategies include:
-
Increased turnout time and pasture access
-
Social interaction opportunities with compatible horses
-
Varied feeding methods to encourage natural foraging behaviors
-
Mental stimulation through toys, obstacles, and changing routines
Behavioral Management Techniques
How to stop horse head bobbing depends heavily on addressing underlying causes while providing appropriate outlets for natural behaviors. Punishment or restraint methods typically worsen the problem and should be avoided.
Positive Reinforcement Training
Training programs focused on signs of a stressed horse recognition help owners identify and address problems before they become entrenched. Positive reinforcement techniques can redirect compulsive behaviors toward more appropriate outlets.
Stress Reduction Strategies
Managing anxiety in horses and stress in horses requires comprehensive approaches that consider physical, mental, and social needs. Consistent routines, appropriate exercise, and social interaction form the foundation of effective stress management.
According to a 2021 study published in the Journal of Veterinary Behavior, horses receiving comprehensive behavioral intervention programs showed 70% improvement in stereotypic behaviors within six months of treatment initiation.
Long-term Management and Monitoring
Successful horse welfare management requires ongoing attention and adjustment. Managing horse behavior is rarely a one-time fix but rather an ongoing process of optimization and refinement.
Dream Horse's commitment to exceptional customer service mirrors the dedication required for successful horse behavior management - consistent attention, quality products, and genuine care for the horse-human relationship. Our equestrian accessories support this journey by providing tools that enhance communication and connection between horses and riders.
Regular monitoring helps identify changes in behavior patterns and allows for prompt intervention when needed. Keeping detailed records of head bobbing while standing, head bobbing while walking, and environmental conditions helps track progress and identify triggers.
Frequently Asked Questions About Horse Head Bobbing
Why do horses bob their heads when standing still?
Head bobbing while standing typically indicates either a stereotypic behavior or an underlying medical issue. Unlike natural movements during activity, stationary head bobbing often suggests boredom in horses, stress in horses, or neurological conditions requiring veterinary attention.
Is horse head bobbing always a sign of lameness?
No, horse lameness head bobbing is just one possible cause. While lameness-related head bobbing typically occurs during movement and corresponds with weight-bearing, many cases of equine head bobbing result from behavioral, neurological, or environmental factors unrelated to limb problems.
Can head bobbing be prevented in horses?
Prevention focuses on proper horse welfare management, including adequate environmental enrichment for horses, appropriate social interaction, and prompt attention to health issues. While genetic predispositions to conditions like headshaking syndrome cannot be prevented, many behavioral causes are entirely preventable through good management.
How serious is headshaking syndrome in horses?
Headshaking syndrome is a serious neurological condition that can severely impact a horse's quality of life. Unlike simple stereotypic behaviors in horses, this condition often requires specialized veterinary treatment and may limit the horse's ability to work or be ridden safely.
When should I call a veterinarian about head bobbing?
Contact your veterinarian promptly if horse head bobbing is persistent, interferes with normal activities, occurs suddenly, or is accompanied by other signs of a stressed horse. Early intervention significantly improves treatment outcomes for most causes of abnormal horse behavior.
Can training help with compulsive head bobbing?
While training cannot cure medical causes of equine head bobbing, appropriate behavioral modification programs can help manage horse stereotypic behavior and equine compulsive behaviors. Success requires addressing underlying welfare issues alongside training interventions.
Understanding horse behavior head bobbing is essential for every horse enthusiast. Whether you're seeking elegant equestrian jewelry to celebrate your passion or practical accessories to enhance your horse care routine, Dream Horse provides quality products that reflect our deep commitment to the equestrian lifestyle. Express your style and assert your individuality while prioritizing your horse's welfare and happiness. 🏆🐴